In recent years, there has been a significant shift in the beauty and skincare industry towards what is known as ‘clean beauty’.
This trend emphasizes the use of natural, non-toxic ingredients that are safe for both consumers and the environment. It reflects a continued pivot toward clean labels and natural ingredients, for which researchers are exploring novel active compounds from plant extracts, marine sources, and biotechnology. These efforts have led to advancements in anti-aging, skin brightening, and protective formulations, among others.
In a trend starting in Europe, US consumers are demanding cleaner and more sustainable beauty products that don’t compromise on quality. The industry is responding from manufacturers to Beyoncé – whose hair care line is positioned as ‘clean’.
Nearly one out of three beauty products are now labeled ‘clean’ in the US and the ‘clean’ beauty market is expected to grow to $15 billion by 2028.¹
Amidst this innovation, water – the most prevalent ingredient in many cosmetic formulations – remains understudied. A search in major cosmetic science journals reveals a scarcity of research on water’s role in cosmetic products, despite its fundamental importance in product stability, ingredient delivery, and overall efficacy.
Discovery of nanobubbles
One of the more promising emerging technologies leveraging water centers around the discovery of nanobubbles. Also known as ultrafine bubbles (UFBs), the field dates to the late 1990s when researchers, equipped with advanced microscopy tools, began to notice the presence of tiny, seemingly stable bubbles in ocean water and streams.
This observation was initially met with skepticism, as traditional understanding suggested that such small bubbles would quickly dissolve due to high internal pressure. However, persistent investigations and refinements in analytical techniques gradually confirmed their existence.
Forming a structure that traps gases and other molecules inside, UFBs were found to be unique in their ability to transport nutrients and gases to cells much more effectively given their immense surface area, negative charge, and high internal pressures.
The UFB field is rapidly expanding. Research publications on UFBs have surged from a few hundred in 2005 to over 3,500 annually. Their applications are evolving just as fast. Initial studies highlighted UFBs' ability to improve water quality, paving the way for their use in water treatment and agriculture – helping plants grow faster, healthier, and with reduced pesticide use.
In addition to these early applications, UFBs are now being explored for their potential in advanced materials and biomedical fields. A 2023 study showed that UFBs can be used as a novel drug delivery system, targeting specific cells and tissues with greater precision compared to traditional methods.²⁻⁴
This sparked a wave of interest in exploring other uses, including personal care, beverages, and even medicine, where microfine bubbles are being investigated for drug delivery. The possibilities of UFBs appear to be limitless. Applications can be appropriate anywhere where nutrients need to penetrate cells more effectively and efficiently. But not all UFBs are created equal.

Next generation UFBs
In efforts to drive product performance through better, cleaner, and faster delivery of active ingredients, researchers at Chicago-based Hydrosome Labs have developed some of the smallest UFBs ever detected.
Hydrosome Labs’ unique ultrafine bubbles, called ‘Hydrosomes’, have significantly higher surface area compared with bubbles in regular water. For example, one trillion ultrafine bubbles fit in a single Champagne bubble, making them superior transporters to cells. And their patented process creates bubbles that are stable in solutions for at least two years, versus six months for other technologies.
“Water is second only to oxygen in importance for survival, yet we often assume it will always behave the same,” says Nick Jackowetz, Chief Science Officer at Hydrosome Labs.
“Throughout history, natural substances have been transformed to better serve society –consider carbon into carbon fiber or silica into computer chips. But what if we could enhance water itself in a natural and sustainable way? That’s exactly what our technology does,” adds Jackowetz.
Applications in skincare
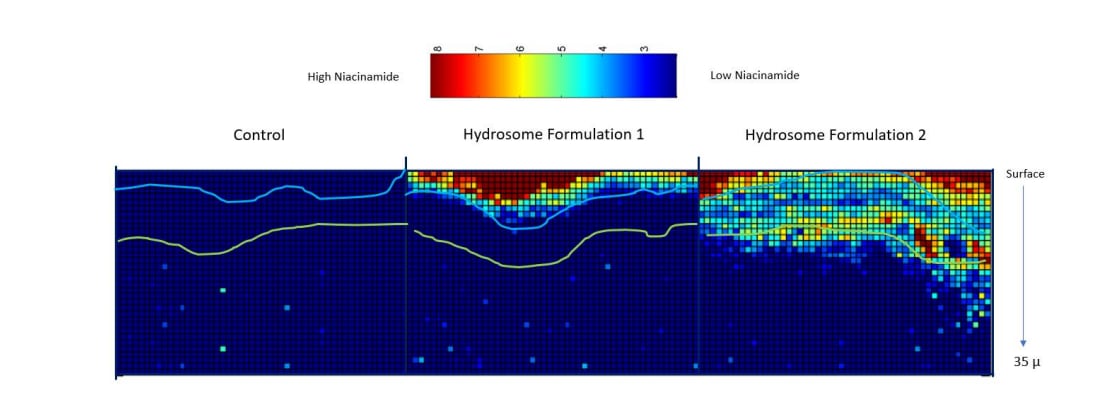
One of the more promising applications Hydrosome Labs is commercializing is in skincare. A study from TRI Princeton and Hydrosome showed niacinamide delivery into the skin was significantly improved versus the control substance (deionized water).⁵
Jackowetz highlights that the study demonstrates how the technology can ‘greatly improve the effectiveness and performance’ of cosmetic ingredients, delivering maximum benefits such as ‘wrinkle reduction, enhanced firmness, improved elasticity, and deeper hydration’.
Earlier research revealed that niacinamide combined with Hydrosome H2O penetrated skin samples two to three times deeper compared to niacinamide mixed with deionized water.
The innovation introduces groundbreaking advancements, setting new benchmarks in its category:
Unmatched stability With a stability of up to two years, this innovation far exceeds the current standard in the nanobubble space, where shelf life typically ranges from four to six months.
Sustainability at its core This patented technology requires no added chemicals or consumables, operates with minimal energy, and prioritizes environmental sustainability.
Simplified formulation By eliminating the need for chemical-based penetration enhancers, this technology allows formulators to create cleaner, more streamlined ingredient statements while mitigating the potential for skin irritation caused by traditional chemicals.
Hydrosome H2O has demonstrated an increase in hydration compared to deionized water. For the first time, this technology transforms water from a simple filler into a ‘super-carrier’, delivering nutrients to challenging areas with unmatched speed and efficiency.
UFB benefits
The technology is compatible with most existing cosmetic formulations and remains stable under extreme conditions, including temperatures as low as 0°C and as high as 121°C during autoclave sterilization cycles – 15 PSI (pounds per square inch) for 15 minutes. It also withstands high shear forces during mixing processes.
Gas selection presents an exciting avenue for exploration. The current UFBs use ambient air (primarily nitrogen and oxygen), but future possibilities could incorporate gases chosen for their cosmetic benefits; oxygen, nitrogen, carbon dioxide, hydrogen, and argon are being investigated.
Another area of focus is ensuring comfort for users. Notably, UFB formulations have been positively received by consumers without reported adverse reactions. To further ensure safety, the UFB technology has achieved self-affirmed GRAS certification through a third-party clinical research organization.
In addition, studies exploring the interactions of UFBs with skin, their impact on skin health, and their relationship with the skin microbiome are in progress to further optimize their benefits for skincare applications.
UFBs enhance the effectiveness of hydrating ingredients like hyaluronic acid and glycerin, along with anti-aging agents such as peptides, vitamins, and antioxidants – promoting skin renewal and collagen production. Cleansers and makeup removers infused with UFBs provide a thorough yet gentle cleanse by effectively lifting impurities without the use of surfactants, helping to reduce skin irritation.
Moreover, UFBs may help to stabilize emulsions and suspensions, reducing the need for additional stabilizers while extending shelf life. This aligns well with the growing consumer demand for clean and minimalist formulations, contributing to more sustainable product development and potentially reducing waste.
Another way-in for the technology involves compounds and active ingredients used in beauty care formulations that are made through processes involving fermentation. This process can not only be less expensive but can also reduce the environmental impact of sourcing some of these rare compounds from sensitive ecosystems.
Hydrosome labs technology can improve the yield and speed of fermentations, making this method of production even more efficient and sustainable.
From a business and supply chain perspective, the technology can be easily integrated for on-site UFB water generation.
In 2024, Meaningful Beauty celebrated its 20th anniversary by introducing Hydrosome H2O as the standout ingredient in its reformulated Youth Activating Melon Serum. This breakthrough technology enhances the serum by delivering best-in-class ingredients more deeply into the skin for improved absorption. Hydrosomes contribute to the product’s ability to visibly plump, firm, and hydrate the skin – transform water from a ‘filler’ to a ‘supercarrier’.
Science-first approach
Hydrosome Labs has invested in taking a science-first approach. Research and development is led by PhD and Master’s level scientists. To date, they have conducted over 100 scientific studies and have collaborated with investigators from leading universities and clinical research labs including University of Chicago, Cornell University, North Carolina State University, TRI Princeton, and IBRL, among others.
Ultrafine bubbles present a novel opportunity for the cosmetics and personal care industry. They offer a unique combination of benefits that address many current industry challenges, from actives delivery to stability to consumer demands for more sustainable and green alternatives.
UFB technology provides formulators with a new tool to create highly effective, environmentally friendly products that meet evolving consumer expectations. This technology shows great potential to be the next significant advancement in cosmetic science, enabling the development of cutting-edge products that combine performance, safety and sustainability.
In October 2024, the team from Hydrosome Labs presented at the world’s leading UFB scientific conference. They have maintained active collaborations with both academic institutions and industry partners to push the limits of UFB technology. Beyond advancements in skincare, their efforts have expanded to include innovations in the fermentation and beverage industries.
“We’re redefining water properties in ways no one thought possible. And this is just the beginning – the potential applications are truly endless,” says Bob Jacobs, President of Hydrosome Labs.
References
- Statista. Market value of clean beauty worldwide from 2021 to 2028.
- Jin, J.; et al. Drug delivery system based on nanobubbles. Wiley Online Library.
- Jia, M.; et al. Nanobubbles in water and wastewater treatment systems: Small bubbles making big difference. Water Research, Volume 245, 2023, 120613.
- Zhang, Y.J.; et al. Progress in research on preparation and application of oxygen nanobubbles in agriculture. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2023, 31(11): 1780−1791.
- Hydrosome Labs. Improved Niacinamide Delivery.


